Using SISCI API with SmartIO devices¶
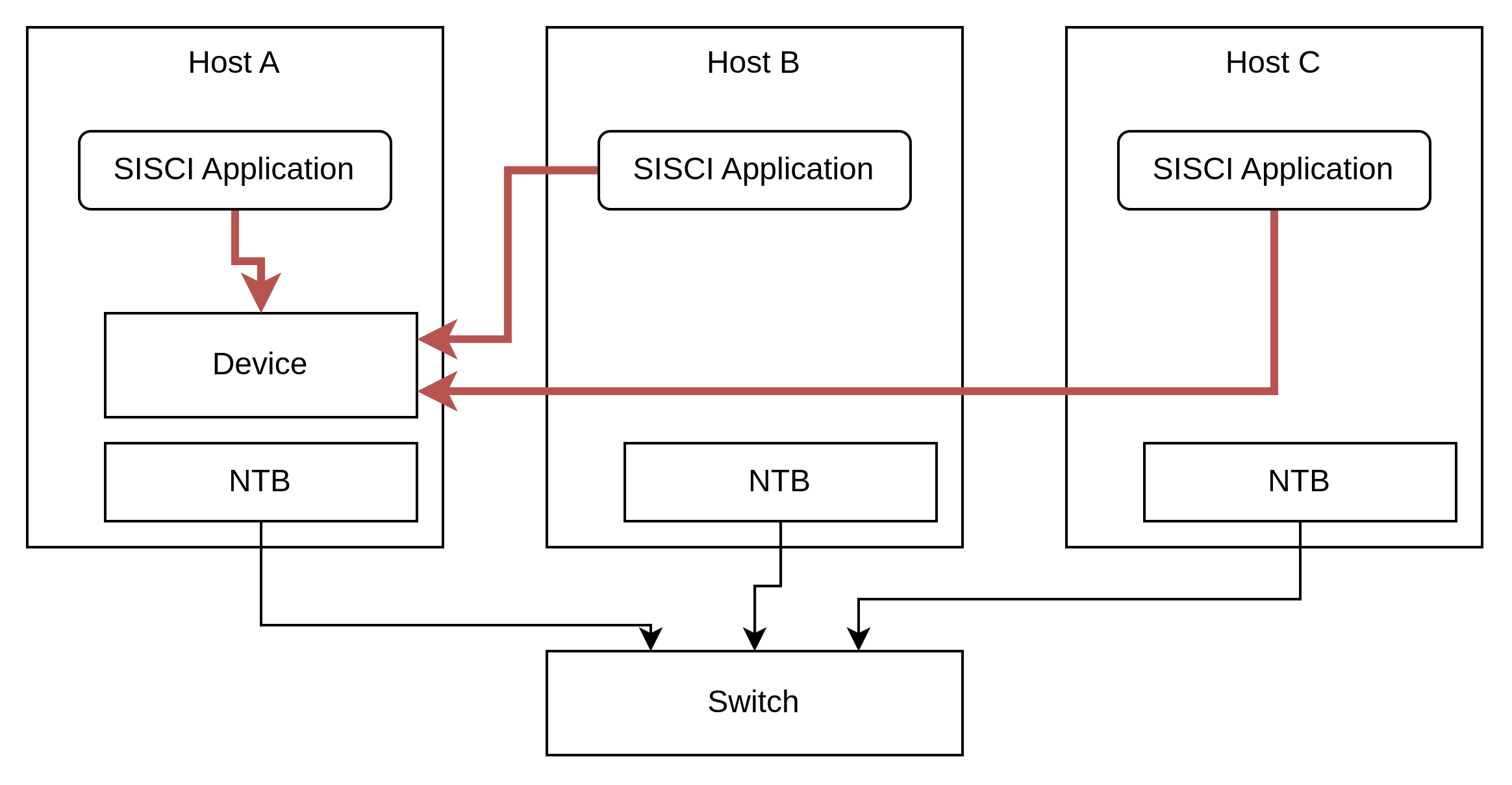
Using SmartIO devices with the SISCI API requires you to develop a device driver against the SISCI API. The effort required to develop a device driver depends on the complexity of the device. This approach is most suited for when you are already familiar with the device-driver interface or if you have an open source driver to reference. While using the SISCI API requires greater effort, it also enables the use of unique functionalities. For example, it allows a device to DMA to a multicast segment where the DMA traffic is replicated by the NTB hardware, duplicating the data to multiple nodes with no additional cost to the device. The device can also map any other segment, including local segments, remote segments and even BAR segments of other devices.
Hint
eXpressWare also exposes a kernel-level API with similar functionality to the SISCI API. It is in fact this API that the dis_nvme driver is built on. If you are interested, please contact support for more information!
Requirements¶
You must have a Dolphin cluster with a topology supported by SmartIO.
The cluster nodes must follow the platform requirements and the lender must support peer-to-peer.
The cluster nodes must run a supported operating system.
You must be prepared to write a device driver yourself.
Additional System Considerations¶
The NTB prefetchable size limits the total size of SISCI segments that a given node can map.
Consider enabling IOMMU on the cluster nodes to protect against rogue DMA accesses from the device.
eXpressWare Installation¶
When installing eXpressWare, make sure to request installation of SmartIO,
either interactively or by passing the --enable-smartio argument. Please refer
to the installation guide for more details.
Lending the device to the Pool¶
The device you want to control with the SISCI API must first be added and made
available with smartio_tool add and smartio_tool available.
The lender must also be connected to all the borrowers with
smartio_tool connect. See Lending Local Devices for more details.
Developing the User Space Device Driver using SISCI API¶
See Writing drivers with SmartIO for an introduction to using the SISCI API for writing device drivers. Note that your device driver application has full access to the rest of the SISCI API so you can for example use PIO to communicate between multiple nodes to coordinate access to the device.